Smart Search: 15
Practical Google Search Operator Use Cases (with Examples)
Google search operators are the secret shortcuts power users and
SEOs rely on to find targeted information fast. Below are 15 real-world use
cases with copy-paste examples you can run now. Use them for audits, competitor
research, link building, outreach, content planning, and lead generation.
Quick note: These operators surface publicly available information.
Use them ethically — don’t scrape private data or spam contacts.
1. Find Possible Indexing Issues (filetype + site)
Operator: site: + filetype:
Example:
site:yourdomain.com filetype:pdf
What it finds: PDFs Google has indexed on your site (useful to spot
gated content accidentally exposed).
Action: If private/gated files are indexed, add x-robots-tag: noindex or restrict access.
2. Discover Competitors & Where They Publish
(related + site)
Operator: related: then site:
Example:
related:moz.com
site:competitor.com/blog
What it finds: Sites similar to a domain and a quick view of where
a competitor publishes content.
Action: Map their content structure and replicate high-performing topics in
your niche.
3. Find Guest Post Opportunities Via Author Footprints
(inurl + author)
Operator: inurl: + author pattern
Example:
"content marketing" inurl:author/jane-doe
What it finds: Pages where a specific author has posted (great for
discovering sites open to guest posts).
Action: Compile target sites and pitch tailored guest posts referencing the
author’s previous topics.
4. Locate Resource Pages (intitle + inurl)
Operator: intitle: + inurl:
Example:
"seo resources" intitle:resources inurl:resources
What it finds: Curated resource pages that may link to helpful
guides.
Action: Pitch your relevant guide or resource for inclusion.
5. Spot Sensitive Files That Shouldn’t Be Indexed
(filetype)
Operator: site: + filetype:
Example:
site:example.com filetype:xls OR filetype:docx
What it finds: Excel and Word documents indexed publicly.
Action: Move sensitive docs behind auth and set proper robots headers.
6. Find Publicly Shared Emails for Outreach (site +
common email patterns)
Operator: site: + string search
Example:
site:twitter.com "gmail.com" "marketing"
What it finds: Tweets where people share email addresses or contact
lines.
Action: Use ethically — verify contact before outreach and avoid mass
unsolicited emails.
7. Internal Link Opportunity Hunting (site + phrase)
Operator: site: + phrase in quotes
Example:
site:yourdomain.com "local seo
tips"
What it finds: Pages on your site that mention a target phrase —
potential sources for internal links.
Action: Add contextual internal links from those pages to your target page.
8. Find Listicles That Don’t Mention Your Brand
(exclude with -)
Operator: phrase + –yourbrand
Example:
"best email marketing tools" –convertkit
What it finds: Comparison/list articles that omit your brand.
Action: Outreach to authors to request inclusion or offer a data-driven angle
to justify a mention.
9. Find Sites Reviewing Your Competitors (allintitle + OR)
Operator: allintitle: + OR
Example:
allintitle:review (mailchimp OR aweber)
What it finds: Pages that include “review” and mention competitors.
Action: Pitch comparative reviews or offer a product demo to the reviewer.
10. Find Quora Threads to Answer (site + inurl)
Operator: site:quora.com inurl:(topic1|topic2)
Example:
site:quora.com inurl🙁seo
| content-marketing)
What it finds: High-interest Quora questions in your niche.
Action: Provide helpful answers with a contextual link back to your resource.
11. Check Competitor Publishing Pace (site + after +
before)
Operator: site: + after: + before:
Example:
site:competitor.com/blog after:2024-01-01 before:2024-12-31
What it finds: How many posts a competitor published in a date
range.
Action: Benchmark and set your own editorial cadence accordingly.
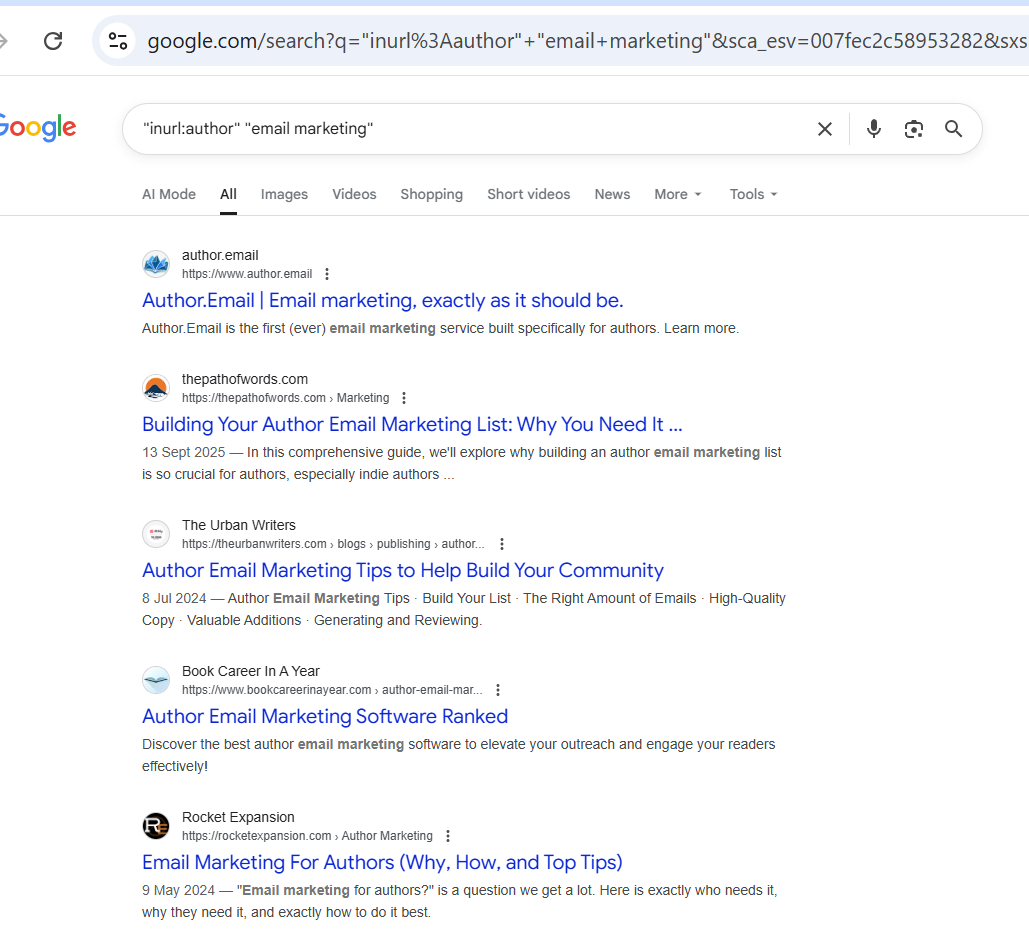
12. Find Author Bios/Guest Posts (inurl:author
+ topic)
Operator: inurl:author + keyword
Example:
"inurl:author" "email marketing"
What it finds: Author pages and contributor footprints across
sites.
Action: Identify prolific contributors to approach for collaborations or link
opportunities.
13. Detect Mentions Without Links (intext + site)
Operator: site: + intext:
Example:
site:industryblog.com intext:"your
brand name"
What it finds: Mentions that may not link to your site (unlinked
brand mentions).
Action: Reach out to request a link — quick link-earning opportunity.
14. Search for Publicly Shared Resumes/Portfolios (filetype:pdf + resume)
Operator: filetype: + keyword
Example:
filetype:pdf "resume" "product manager"
What it finds: Candidate resumes and portfolios that include
contact info.
Action: Recruit talent or freelance partners for projects.
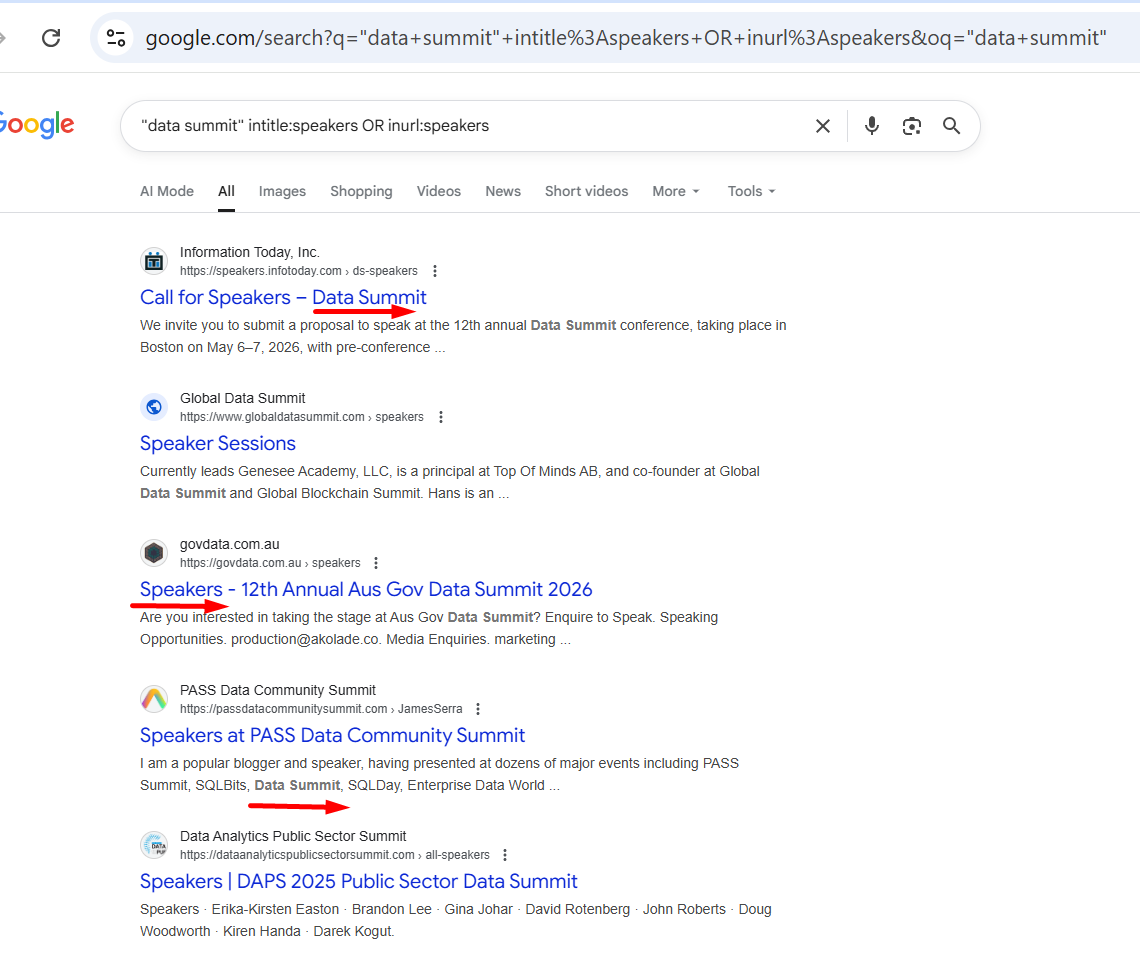
15. Find Event Pages & Speaker Contacts (site +
"speakers" or "contact")
Operator: keyword + intitle: or inurl:
Example:
"data
summit" intitle:speakers OR inurl:speakers
What it finds: Event speaker lists and organizer contact pages.
Action: Pitch speaking opportunities or partnerships; gather high-value B2B
leads.
Quick Tips & Best Practices
- Combine operators creatively.
For example, find resources on competitor sites that don’t link to you:
- site:competitor.com intitle:resources
–yourbrand
- Use filetype: to find
whitepapers, case studies, or PDFs that could reveal gated content
accidentally indexed.
- Pair with tools like Ahrefs Content Explorer or Site Explorer for traffic
estimates and backlink data when scaling research.
- Respect privacy & laws.
Never harvest personal data for spam — aim for value-first outreach and
opt-in methods.
- Save queries you use often in a
document so team members can repeat audits quickly.
Final Word
Mastering Google search operators multiplies your research speed
and accuracy. Whether you’re diagnosing indexing problems, scraping resource
pages for link opportunities, hunting guest-posting targets, or finding
outreach contacts — these operators are indispensable. Start by trying 3–4 of
the examples above and expand into combinations once you’re comfortable.