Adopting the Future of
Search: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Strategies for Success
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, a new approach to
search engine optimization (SEO) has emerged: Generative Engine Optimization
(GEO). As we navigate this uncharted territory, it’s essential to understand
the benefits, key strategies, and implementation techniques of GEO.
So, what is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)? In
essence, GEO is the practice of building clean, documented
"interfaces" for large language models, enabling them to discover,
extract, and cite content with minimal friction. This approach marks a
significant shift in focus, transitioning from ranking on search results pages
to becoming the trusted data source for AI-powered engines ¹.
The benefits of GEO are numerous, and they can be summarized as follows:
– Increased Reach: By optimizing
for generative AI, you can increase visibility beyond traditional search
engines.
– Enhanced User Experience: GEO
optimizes content to provide quick, relevant, and personalized answers, thereby
improving user satisfaction and loyalty.
– Competitive Advantage: Early
adoption of GEO practices creates authority signals that compound over time,
building stronger positions in AI recommendation systems.
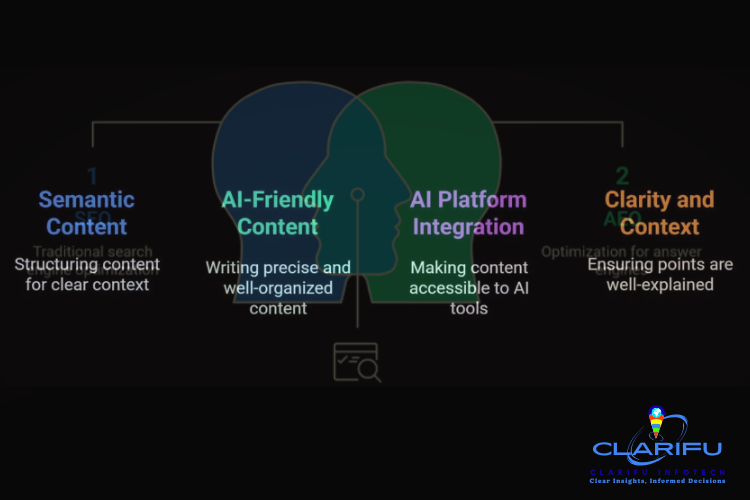
To implement GEO effectively, consider the following key strategies:
– Semantic Structure &
Markup: Utilize semantic elements, such as <header>, <main>, and
<section>, to provide a clear structure for your content.
– Structured Data & Schema
Implementation: Implement (link unavailable) markup to provide explicit types
and relationships for your content.
– Content Architecture for AI:
Organize pages like microservices, with each topic cluster becoming a content
module.
– Entity Optimization &
Knowledge Graphs: Tag entities consistently across pages to maintain
referential integrity inside the model’s knowledge graph.
In terms of technical implementation techniques, focus on the following:
– Frontend GEO Implementation:
Use explicit HTML5 elements and attach structured data to provide a clear
interface for AI crawlers.
– Backend GEO Architecture:
Expose structured context through a lightweight metadata endpoint.
– Testing Your GEO
Implementation: Automate verification using tools like Jest and Puppeteer to
ensure semantic markup and structured data are correct.
To take your GEO strategy to the next level, consider the following
advanced techniques:
– Automating GEO Optimization:
Wire verification into CI/CD pipelines to ensure structured data is correct and
up-to-date.
– Scaling GEO Across Systems:
Centralize schemas in a shared package and version them to ensure consistency
across distributed architectures.
What we can Conclude?
In conclusion, by embracing Generative Engine Optimization
(GEO) and Search Engine Optimization, you can unlock new opportunities for
visibility, credibility, and authority in the AI-driven search landscape.
Remember to focus on semantic structure, structured data, content architecture,
and entity optimization to ensure your content is discoverable, extractable,
and citable by AI-powered engines.

